ddd
Operation
Perform a single operation on 2 variables, or just numbers directly, example:

Let’s say a is 10, therefore this operation means 10 + 5result will then be 15
+
Addition
-
Subtraction
*
Multiplication
/
Division
//
Integer division, like division but it will round down the results
%
Modulo operation, like division but it returns the remainder
^
Power / exponentiation
Sqrt
Square root
==
Check if the 2 variables are equal to each other
Returns 1 or 0 / true or false
Not
Logical not, check if the 2 variables are not equal to each other
Returns 1 or 0 / true or false
And
Logical AND gate
Inputs and output are boolean
<
Less than, check if the first variable is less than the second variable
Returns 1 or 0 / true or false
>
Less than equal, check if the first variable is less than equal the second variable
Returns 1 or 0 / true or false
>=
Greater than, check if the first variable is greater than the second variable
Returns 1 or 0 / true or false
>=
Greater than, check if the first variable is greater than the second variable
Returns 1 or 0 / true or false
log
Logarithm, return the exponent given the base and the result
log 10
Logarithm in base 10
floor
Floor , Round down the specified number
ceil
Ceiling , Round up the specified number
or
Bitwise or
b-and
Bitwise and
XOR
Bitwise XOR
flip
Bitwise flip
max
return the largest number out of the 2 number
min
return the smallest number out of the 2 number
angle
Angle of vector in degrees,usually used like: Angle = ((x1-x2) (y1-y2))
internally the code does:
ang1 = atan2(a,b) * 180/π (convert into degrees)
result = { if ang1 < 0 = (ang1 + 360), otherwise = (ang1) }
where a is the first variable and b is the second
angle diff
Absolute distance between to angles in degrees, usually used like: angdiff = (ang1)(ang2)
innternally the code does:
a = a % 360
b = b % 360
d1 = (a - b + 360) % 360
d2 = (b - a + 360) % 360
result = min(d1, d2)
where a is the first variable and b is the second
len
Length of vector, usually used like: len = ((x1-x2) (y1-y2)).
internally the code does:
result = √ (a a + b b)
where a is the first variable and b is the secondnoise
noise
2d simplex
takes 2 value as coordinates and outputs a value from -1 to 1
unlike rand, noise is detemernistic, which means a pair of coordinates will always outputs the same result
for more information to how it internally works check https://github.com/Anuken/Arc/blob/master/arc-core/src/arc/util/noise/Simplex.java the "raw2d" function/method
rand
generate a random float in range of 0 to the specified value
sin
Sin, in degrees
cos
Cos, in degrees
tan
Tan, in degrees
asin
Asin, in degrees
atan
Atan, in degrees
atan
Atan, in degrees
Lookup
Look up an item/liquid/unit/block type by ID.
Total counts of each type can be accessed with:@unitcount / @itemCount / @liquidCount / @blockCount, which is :
56 / 22 / 11 / 254 (as of v146), respectively, they are a constant.
For the inverse operation, sensor @id of the object
Example:
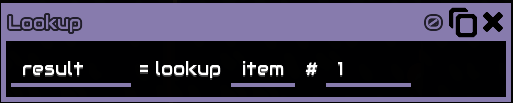
This operation is looking up item with an id of 1, which is lead, thereforeresultwill then be@lead, acontent name, which can be used for things like sensor :
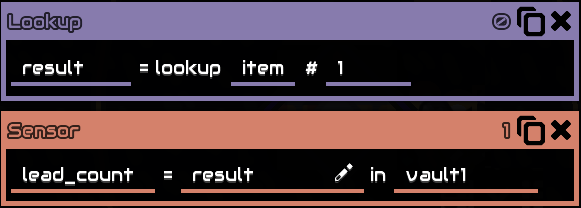
lead_countis now a variable containing number of lead invault1
Lookup are usually used with anincrementing variable
Lists of IDs can be found in theAppendix
Pack Color
Packs RGBA color into a single number, is usually used with draw col and control color
Since it's a single number it can be stored to 1 address on cells/banks, instead of 4 addresses with the usual RGBA, making reading and writing a lot easier too.

RGBA is their respective color, can also be directly written with a number, value is from 0 (dimmest) to 1 (brightest) You can unpack a Packed color by dividing it by %00000001, this will return 32-bit unsigned integer, 8 bits for each value, example : a 255,255,255,255 color when unpacked will return 4294967295, which is the maximum value of 32-bit unsigned integer, converting it to binary will return 11111111111111111111111111111111 ( 8 bit for each value ), by using the bit shift right operation and bitwise and operation you can extract each color value.
Wait
Wait the specified number of seconds, in other words, pausing the processor for that amount of seconds
Stop
Completely stops the processor from running, cannot be resumed in any way other than rebuilding or refreshing the code, to pause a processor disable it instead using control enable
End
End the process, when a processor run this line it will go back to 0 as if it reach the end of the instruction, similar to jump always 0
Jump
Jump to a line number on the processor with a condition
if condition are true jump to the specified line, if false does not jump (continuing to instruction below it
==
Check if the 2 variables are equal to each otherNot
Logical not, check if the 2 variables are not equal to each other<
Less than, check if the first variable is less than the second variable<=
Less than equal, check if the first variable is less than equal the second variable>
Less than equal, check if the first variable is less than equal the second variable>=
Greater than equal, check if the first variable is greater than equal the second variable===
Strict equal, usually used to check for null, example:
0 null is true, while 0 = null is falseAlways
Always jump regardless