Instructions
Read
Read a value from a cell
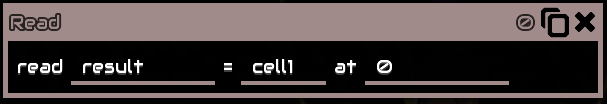
resultis your variable namecell1is where to get the value from, a building reference, “bank{number}” for Banks0 is the cell’s address. like said above, cells can store up to 64 values, this means there are only 64 addresses, starting at0, meaning0-63
Example: there is a value at 0 incell1that is10, thenresultvariable will be10
Write
Write a value to a cell
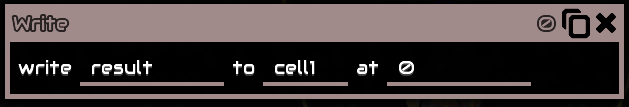
Essentially the same with read but it writes instead
Example: the result variable is 10, then it will write 10 to cell1 at #0
Can also be directly written using a number instead of a variable.
Draw
Adds a command to the draw buffer
Clear
Sets the entire screen to a specific color
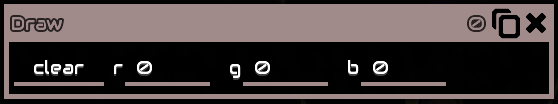
RGB stands for Red,Green,Blue
Value can be from 0 (dimmest) to 255 (brightest)
Example: 255, 255, 255 is White
Color
Sets the color of the next upcoming draw isntruction

RGBA stands for Red,Green,Blue,Alpha
To put it simply Alpha is Opacity, it is how opaque the next draw instruction will be
0 is 0% and 255 is 100% opaque
Value can be from 0 (dimmest) to 255 (brightest)
col
Same as color, but use hex color code instead of RGB color code
Usually used with the Pack Color instruction
Stroke
Sets the line width for any upcoming draw operationsns
Line
Draws a line from one coordinates to another coordinates
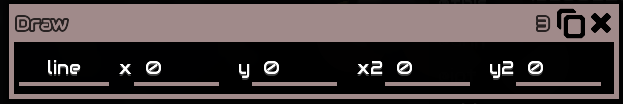
x, y is the first set of coordinatesx2, y2 is the second sets of coordinates
Rect
Draw a rectangle at the specified coordinates with the bottom left of the rectangle as its originn

x, y is the rectangle coordinateswidth and height are the rectangle width and height
Line Rect
Same as rect, but only draws the outline of the rectangle
Poly
Draw a polygon with its center as its origin
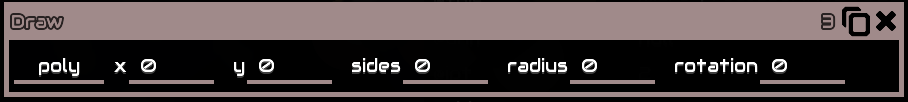
x, y is the polygon coordinatessides is the number of sides the polygon will haveradius is the radius of the polygonrotation will rotate the polygon, in degrees
Line Poly
Same as poly, but only draws the outline of the polygon
Triangle
SDraws a triangle with 3 different sets coordinates as its vertices
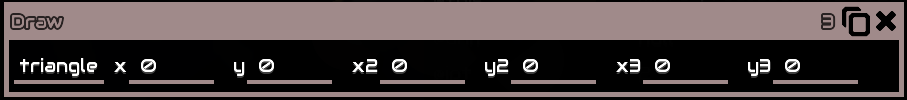
x, y is the first sets of coordinatesx2, y2 is the second sets of coordinatesx3, y3 is the second sets of coordinates
Image
Draws an image of something from the game with content name, such as@daggeror@copperwith its center as its origin,
if it draws a picture of (oh no) that means whatever you're trying to draw either doesn't exist or not supported, the only work around is drawing it manually, though the Bleeding Edge version supports more content

x, y is the of coordinatesimage is what image it will draw, you put object name here, like @daggersize is the size of the imagerotation will rotate the image, in degrees
cannot draw modded items!
Draw Flush
Flush the queued draw instruction(s) from the draw buffer to the specified displays with its building reference
\n
Writing \n will write the next text to a new line, example:

Printing colors “ [ ] "
You can change printed colors with [ ], example
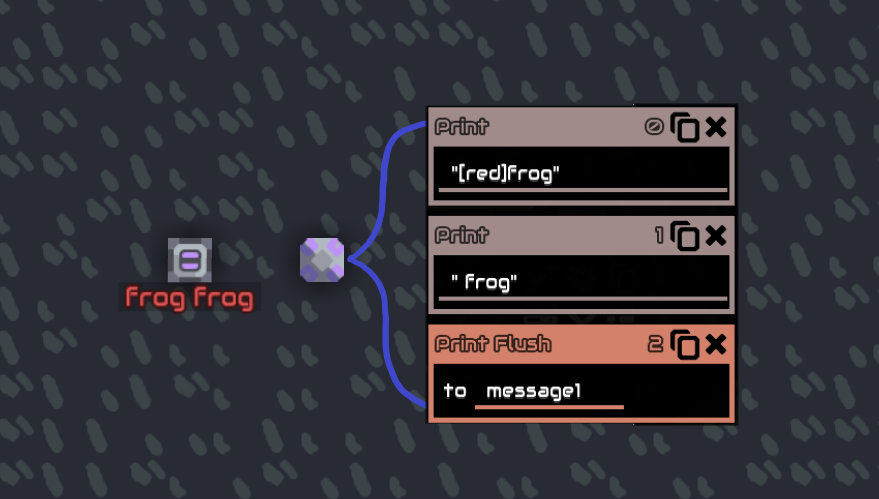
You can either put color names or hexadecimal color code
Example of HEX color code is #FF0000 for red, you can simply search “hex color picker” on google to choose your own color
Emoji/icons
You can change printed colors with [ ], exampleNot really Mlog related but worth mentioning,
Mindustry utilizes a specific range within the private use area of Unicode, these can be found on the source code : https://github.com/Anuken/Mindustry/blob/9eb8492f4ab8daf15685128229489b7229cc1048/core/assets/icons/icons.properties#L4
which are:
these might just look like boxes to you, but they are actually valid characters when pasted into the game
other than this, Mindustry also supports some public unicode characters, though what of and in what range is unknown , attempting to paste unsuported characters will just show nothing.
Here what they look like in game:
Print Flush
Flush the queued print instruction(s) from the text buffer to the specified message block with its building reference, will erases previous message on the message block
Get link
Get link gets the link of the processor linked building
example : you have 2 buildings linked to the processor, duo1 and duo2
getlink result #0 will get you duo1 and
getlink result #1 will get you duo2
The order is based on the order you link the buildings
The buildings reference is then result
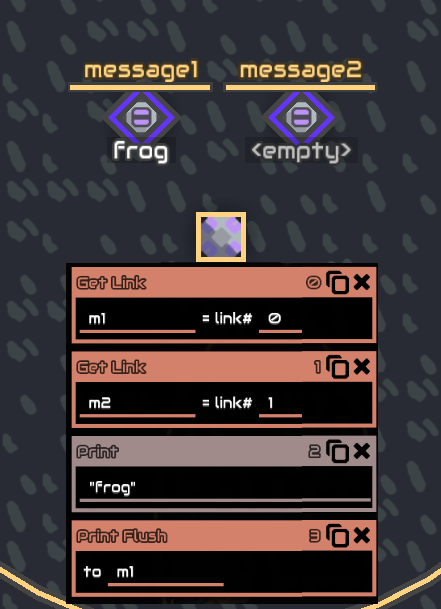
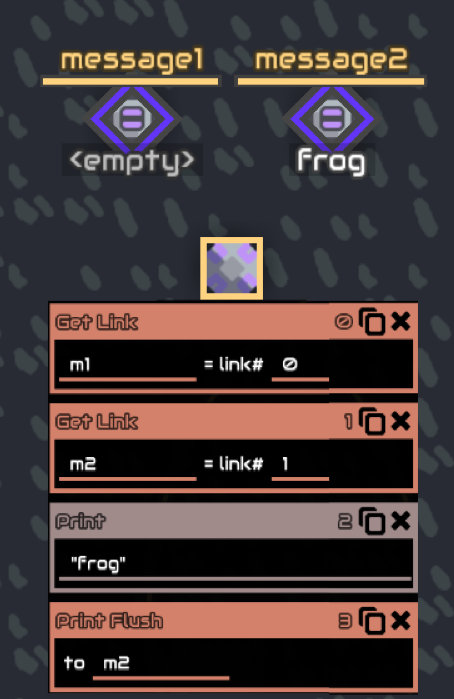
Using it with numbers is pretty useless, they are usually used with incrementing variables as its index, this way you can get multiple buildings without writing every building reference (message1,2,3….)
Control
Controls a building of a building reference or a unit reference
Enabled
Enabled or disable a building, can be 0 or 1 or true and false

of a block referenceto (state), 1 / true enable, 0 / false disable,
when disabling a processor it pauses code execution until re-enabled again, resuming at the line number where it was disabled
here is a list of blocks behaviour when disabled
Shoot
Shoot at a unit/building but with velocity prediction
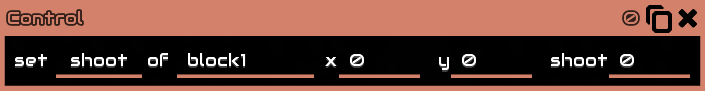
x and y is coordinate location where to aim/shoot atshoot 0 or 1, true or false, if true tells the turret/unit to shoot, if false stop shooting
Shoot
Shoot at a unit/building but with velocity prediction

unit, what object to aim/shoot at, it says "unit" but you can put a building reference there too.shoot 0 or 1, true or false, if true tells the turret/unit to shoot, if false stop shooting
Config
Change the configuration of buildings,
for example :
sorter config, by putting item name to thetoarguments, eg@copper,@lead,@surge-alloy
unit factory config, by putting unit name to thetoarguments, eg@flare,@dagger, and of course it only supports units it meant to create, if you put other unit name that it cant create it will just deselect all unit
Color
Change the color of Illuminator block Usually used with pack color
Radar
Radar a unit in range of the building’s range

from is building referencetarget is a filter, target enemy means it will only radar enemy unitsorder is sorting order, ascending or descending, can only be 0 or 1sort is a metric to sort results by, sort distance means it will get unit by distance
In this example, since order is 1, and sort is distance, the unit returned is the closest to that building.
Cannot get multiple units at the same time.Order cannot be change to look for metrics in the middle e.g 0.5
Will output the unit reference to result
Sensor
Sensor / get / read data from an object, usually buildings or units with their reference

result is your named variable@copper is what data to get from the specified object, can be a unit or a building. (click the pencil icon beside it for a list of sensorable data alternatively see Sensors for a list with explanation on each one)block1 building reference, it is what object to get the data from, can also be a unit reference
Example:

This will get the amount of copper in vault1, the number will be stored in the variable result, let’s say the vault has 10 coppers, therefore result will be 10
Set
Set a variable, either with numbers or with another variable (including unit or block reference)
Operation
Perform a single operation on 2 variables, or just numbers directly, example:

Let’s say a is 10, therefore this operation means 10 + 5result will then be 15
+
Addition
-
Subtraction
*
Multiplication
/
Division
//
Integer division, like division but it will round down the results
%
Modulo operation, like division but it returns the remainder
^
Power / exponentiation
Sqrt
Square root
==
Check if the 2 variables are equal to each other
Returns 1 or 0 / true or false
Not
Logical not, check if the 2 variables are not equal to each other
Returns 1 or 0 / true or false
And
Logical AND gate
Inputs and output are boolean
<
Less than, check if the first variable is less than the second variable
Returns 1 or 0 / true or false
>
Less than equal, check if the first variable is less than equal the second variable
Returns 1 or 0 / true or false
>=
Greater than, check if the first variable is greater than the second variable
Returns 1 or 0 / true or false
>=
Greater than, check if the first variable is greater than the second variable
Returns 1 or 0 / true or false
log
Logarithm, return the exponent given the base and the result
log 10
Logarithm in base 10
floor
Floor , Round down the specified number
ceil
Ceiling , Round up the specified number
or
Bitwise or
b-and
Bitwise and
XOR
Bitwise XOR
flip
Bitwise flip
max
return the largest number out of the 2 number
min
return the smallest number out of the 2 number
angle
Angle of vector in degrees,usually used like: Angle = ((x1-x2) (y1-y2))
internally the code does:
ang1 = atan2(a,b) * 180/π (convert into degrees)
result = { if ang1 < 0 = (ang1 + 360), otherwise = (ang1) }
where a is the first variable and b is the second
angle diff
Absolute distance between to angles in degrees, usually used like: angdiff = (ang1)(ang2)
innternally the code does:
a = a % 360
b = b % 360
d1 = (a - b + 360) % 360
d2 = (b - a + 360) % 360
result = min(d1, d2)
where a is the first variable and b is the second
len
Length of vector, usually used like: len = ((x1-x2) (y1-y2)).
internally the code does:
result = √ (a a + b b)
where a is the first variable and b is the secondnoise
noise
2d simplex
takes 2 value as coordinates and outputs a value from -1 to 1
unlike rand, noise is detemernistic, which means a pair of coordinates will always outputs the same result
for more information to how it internally works check https://github.com/Anuken/Arc/blob/master/arc-core/src/arc/util/noise/Simplex.java the "raw2d" function/method
rand
generate a random float in range of 0 to the specified value
sin
Sin, in degrees
cos
Cos, in degrees
tan
Tan, in degrees
asin
Asin, in degrees
atan
Atan, in degrees
atan
Atan, in degrees
Lookup
Look up an item/liquid/unit/block type by ID.
Total counts of each type can be accessed with:@unitcount / @itemCount / @liquidCount / @blockCount, which is :
56 / 22 / 11 / 254 (as of v146), respectively, they are a constant.
For the inverse operation, sensor @id of the object
Example:
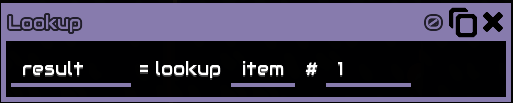
This operation is looking up item with an id of 1, which is lead, thereforeresultwill then be@lead, acontent name, which can be used for things like sensor :
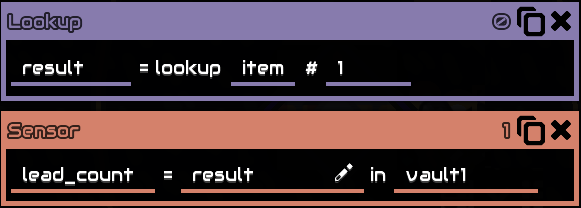
lead_countis now a variable containing number of lead invault1
Lookup are usually used with anincrementing variable
Lists of IDs can be found in theAppendix
Pack Color
Packs RGBA color into a single number, is usually used with draw col and control color
Since it's a single number it can be stored to 1 address on cells/banks, instead of 4 addresses with the usual RGBA, making reading and writing a lot easier too.

RGBA is their respective color, can also be directly written with a number, value is from 0 (dimmest) to 1 (brightest) You can unpack a Packed color by dividing it by %00000001, this will return 32-bit unsigned integer, 8 bits for each value, example : a 255,255,255,255 color when unpacked will return 4294967295, which is the maximum value of 32-bit unsigned integer, converting it to binary will return 11111111111111111111111111111111 ( 8 bit for each value ), by using the bit shift right operation and bitwise and operation you can extract each color value.
Wait
Wait the specified number of seconds, in other words, pausing the processor for that amount of seconds
Stop
Completely stops the processor from running, cannot be resumed in any way other than rebuilding or refreshing the code, to pause a processor disable it instead using control enable
End
End the process, when a processor run this line it will go back to 0 as if it reach the end of the instruction, similar to jump always 0
Jump
Jump to a line number on the processor with a condition
if condition are true jump to the specified line, if false does not jump (continuing to instruction below it
==
Check if the 2 variables are equal to each otherNot
Logical not, check if the 2 variables are not equal to each other<
Less than, check if the first variable is less than the second variable<=
Less than equal, check if the first variable is less than equal the second variable>
Less than equal, check if the first variable is less than equal the second variable>=
Greater than equal, check if the first variable is greater than equal the second variable===
Strict equal, usually used to check for null, example:
0 null is true, while 0 = null is falseAlways
Always jump regardless